Samsung’s 2nm Breakthrough Could Rewrite the Chipmaking Battle with TSMC
Samsung is stepping into a new era of semiconductor excellence. After years of playing catch-up with Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC), the South Korean giant is now poised to deliver a major technological comeback – one that could reshape the performance of its future Galaxy smartphones, including the much-anticipated Galaxy S26 Ultra.
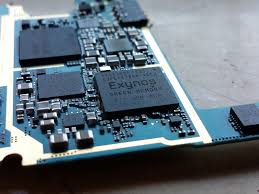
The turning point lies in Samsung Foundry’s rapid recovery and innovation in chip fabrication. Following a difficult 2024 marked by yield issues in its 3nm process, Samsung has apparently overcome its production hurdles. The company was forced to rely on Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 8 Elite chips across the Galaxy S25 lineup, abandoning its in-house Exynos 2500 due to poor yields. But that chapter seems to be closing. Samsung’s engineers have achieved a near 70 percent yield rate on their next-generation 2nm process – a figure that could not only restore confidence but place the company ahead in the global race for chip supremacy.
The upcoming Exynos 2600, built on this advanced 2nm architecture, symbolizes more than a technical win – it marks a cultural revival for Samsung’s semiconductor division. After four years of hesitation, the company is bringing back Exynos to its top-tier Ultra models. This signals a belief that its chips are not just competitive but potentially superior in specific efficiency and performance areas when compared to Snapdragon’s latest offerings. If benchmarks and early reports hold true, users can expect faster processing, improved energy efficiency, and better AI computation power, thanks to the denser and more efficient transistor design.
For Samsung, the implications stretch far beyond its Galaxy lineup. A successful 2nm process at competitive costs could draw back partners who migrated to TSMC when Samsung’s yields faltered. Industry insiders suggest that the combination of improved performance and more affordable foundry pricing could make Samsung an attractive alternative for clients producing high-performance chips for various markets, including mobile, automotive, and AI computing.
The 70 percent yield target is no small feat – it reflects years of research, new manufacturing techniques, and refined extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography. If Samsung achieves or exceeds this milestone before 2026, it won’t just catch up with TSMC; it might outpace it in critical areas of efficiency and cost-per-wafer.
As confidence returns, the ripple effects could be transformative. A revitalized Exynos brand would mean Samsung could potentially emulate Apple’s success with its integrated silicon ecosystem. A future where Samsung controls both hardware and chip architecture could lead to more seamless optimization across its devices – from Galaxy phones to tablets and even laptops. In the long term, this 2nm success might mark the start of Samsung’s “Apple silicon moment,” a rebirth that redefines its technological independence and innovation leadership.
1 comment
they said 2nm by 2026, that’s fast af 😮