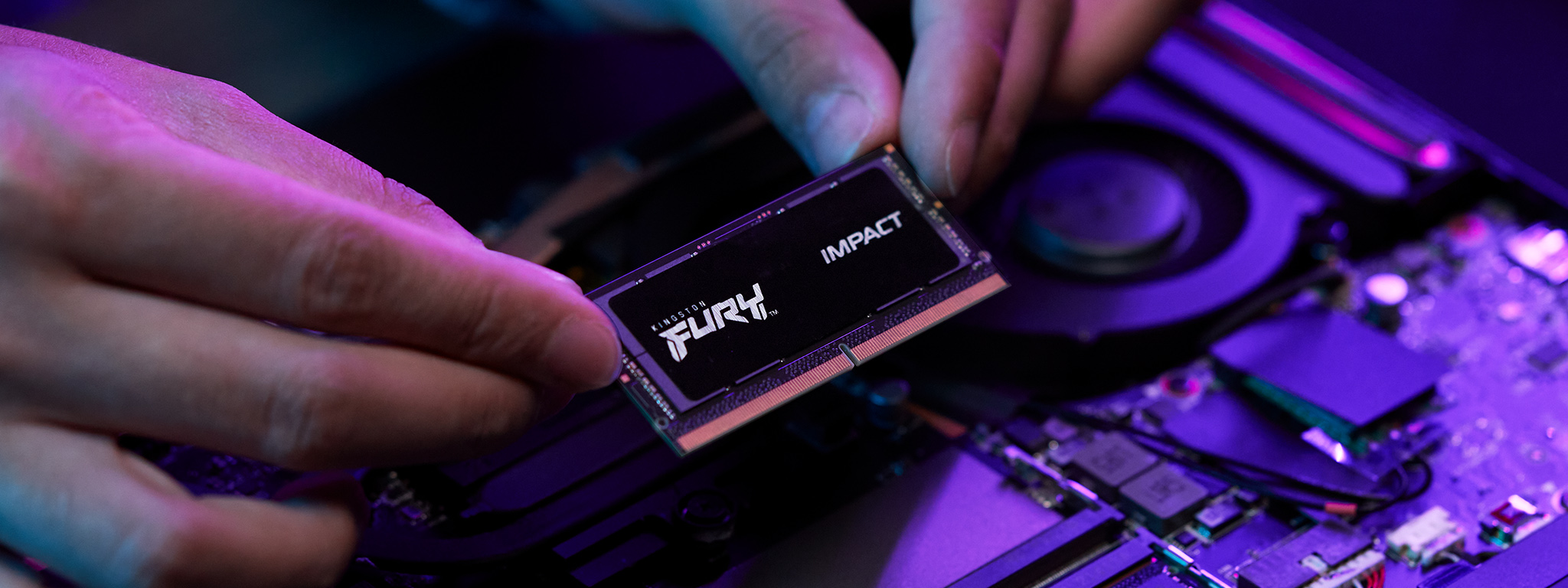
How to Increase RAM in a Laptop: Complete Guide for Better Performance
Laptops are excellent tools for work, gaming, and everyday tasks, but their performance often hinges on one critical factor: RAM (random access memory). RAM acts as a temporary workspace for the system, allowing programs, games, and browsers to run smoothly. When it runs out, you face freezing screens, crashing software, and painfully slow load times. The good news is, instead of replacing your laptop entirely, you can often breathe new life into it by upgrading or expanding the RAM.
When Do You Actually Need More RAM?
Not every slowdown is caused by insufficient memory, so identifying the true bottleneck is essential. A laptop may stutter for many reasons: an old hard drive, an overheating CPU, or even malware. However, there are specific telltale signs that RAM is the culprit.
- Frequent Freezing During Heavy Tasks: If applications like Photoshop, video editors, or modern games hang the system, this is a red flag. Opening many browser tabs can also trigger slowdowns if memory is saturated.
- Error Messages from Software: Some programs explicitly tell you they cannot continue because available memory is too low. Professional tools like DaVinci Resolve or Adobe After Effects often display RAM warnings during complex projects.
- Task Manager Monitoring: On Windows, pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc opens the Task Manager. There, under “Performance → Memory,” you can see RAM usage in real-time. If usage consistently spikes above 75–80%, your system is operating at the edge, and even one more open tab can push it over.
The key is to measure during actual use: launch the software that usually causes issues, then check which resource maxes out. If memory is always high while CPU remains moderate, adding RAM is your most effective upgrade.
Can Every Laptop’s RAM Be Expanded?
Unfortunately, not all laptops allow memory upgrades. Many slim ultrabooks, 2-in-1 convertibles, and nearly all modern MacBooks since 2012 have soldered RAM that cannot be changed. In contrast, gaming laptops and most mainstream models typically include slots for expansion.
To check compatibility, confirm these details:
- Slots Available: Your laptop may have one or two RAM slots. Some models ship with one slot occupied and leave the other free. Others use a hybrid approach: part soldered memory, plus one free slot for upgrades.
- Maximum Supported Capacity: Each laptop motherboard has a maximum supported RAM. For example, a device might officially support up to 32 GB, but ship with only 8 GB installed. This information is listed in the technical specifications on the manufacturer’s website or product page.
- Access Options: Look for whether the RAM compartment is under a small service hatch (common in older models) or behind the full back panel (common today). Some brands, like Lenovo ThinkPads, make upgrades straightforward, while others, like Apple, block them entirely.
Choosing the Right RAM: Key Parameters to Consider
Upgrading RAM isn’t as simple as buying any stick. Laptops use compact modules and are picky about formats. Let’s break down the main criteria:
1. Form Factor
Laptops use SO-DIMM modules, which are shorter and slimmer than desktop DIMMs. Buying the wrong size means it won’t physically fit.
2. RAM Generation
Different generations of RAM are not interchangeable. The most common today are DDR4 and DDR5. Older laptops may use DDR3 or even DDR2. Each generation has a unique notch position, so they cannot be swapped. Always check the current generation of your laptop’s memory via Task Manager, CPU-Z, or the manufacturer’s specification sheet.
3. Module Count and Dual-Channel Benefits
Laptops often benefit from using two identical sticks instead of one. Dual-channel mode effectively doubles data transfer bandwidth, providing anywhere from a modest 5% boost in everyday apps to a near 100% improvement in memory-hungry workloads. For example, two 16 GB sticks can outperform a single 32 GB stick, despite offering the same total capacity.
4. Frequency and Timing
RAM frequency (measured in MHz) affects performance. Ideally, match the frequency of existing modules. If modules differ, they will run at the speed of the slower one. For example, mixing 1600 MHz with 1866 MHz modules results in both operating at 1600 MHz. While mixing works, optimal performance comes from matched pairs.
5. Capacity
Determine how much RAM you actually need. For most everyday users, 8 GB is sufficient. For gamers and creative professionals, 16 GB to 32 GB provides noticeable headroom. Heavy-duty users – video editors working with 4K or 8K footage, developers running multiple virtual machines – may require 64 GB or more, but only if the motherboard supports it.
Tools for Identifying Current RAM Specs
Before shopping, identify exactly what’s installed. Free utilities like CPU-Z or AIDA64 reveal the capacity, generation, and frequency of your modules. Alternatively, on Windows, open “System Information” to see installed memory, then cross-check with the manufacturer’s website to learn the maximum supported upgrade.
How to Physically Install New RAM
Once you’ve confirmed compatibility and purchased the right modules, installation can be straightforward. However, proceed carefully to avoid damaging sensitive parts.
- Check Warranty Terms: Some manufacturers void warranties if you open the laptop. If your device is still covered, confirm policies before proceeding. Authorized service centers can upgrade RAM while preserving the warranty.
- Shut Down and Remove Battery: Always power off the laptop and disconnect the charger. If the battery is removable, take it out to avoid electrical accidents.
- Access RAM Slots: Remove the back cover or dedicated RAM hatch. Keep screws organized – many laptops use multiple sizes, and mixing them up can cause assembly problems later.
- Remove Existing Modules: If replacing, push back the side latches holding the old stick. It will pop up at an angle, allowing easy removal.
- Insert New Module: Align the notch of the new RAM stick with the slot, slide it in at a 30-degree angle, and press down until the latches click.
- Reassemble and Test: Replace the cover and screws. Boot the laptop and check “System Properties” or Task Manager to confirm the new memory is recognized.
Practical Upgrade Examples
Consider a mid-range gaming laptop with 8 GB of DDR4 memory in a single slot. By adding a second identical 8 GB stick, you achieve 16 GB total capacity and enable dual-channel mode. The result: smoother gameplay in titles like GTA V or Cyberpunk 2077, and fewer stutters when streaming simultaneously.
Or take a student laptop used for heavy research with dozens of browser tabs. Doubling from 4 GB to 8 GB ensures smoother multitasking and less reliance on slow virtual memory stored on the hard drive.
Limitations and Alternatives
What if your laptop’s RAM is soldered? Unfortunately, upgrades aren’t possible. In this case, optimizing performance relies on alternatives:
- Upgrade to an SSD: Replacing a mechanical hard drive with an SSD drastically improves responsiveness, reducing reliance on RAM by speeding up swap files.
- Close Unnecessary Apps: Browser tabs, background chat programs, and auto-start apps all consume memory. Trim them to free up resources.
- Virtual Memory Adjustments: Windows allows adjusting pagefile settings, effectively expanding usable memory with disk space, though at slower speeds.
Step-by-Step Recap
- Check performance via Task Manager to confirm RAM shortage.
- Confirm upgrade options by reviewing your laptop’s specs.
- Select SO-DIMM modules of the correct generation and frequency.
- Prioritize dual-channel setup with matched sticks for best results.
- Install carefully, following warranty considerations and safety steps.
Final Thoughts
Expanding laptop RAM is among the most cost-effective ways to extend its useful life. For gamers, creators, and professionals, it transforms sluggish machines into responsive workhorses. While limitations exist – particularly in soldered models – those with accessible slots can often double or quadruple memory with minimal effort. Combined with an SSD upgrade, even a five-year-old laptop can feel brand new.
1 comment
why do they even sell laptops with 4gb in 2025… useless